Do you know what are the commonly used insulation boards? They are FR4, 3240 epoxy board, bakelite board, PI polyimide board, electrical laminate, and GPO-3 sheet. Below we will introduce the characteristics and applications of these six insulation materials one by one.
Composition: Made of epoxy resin and fiberglass cloth through a lamination process.
Core Features:
Stable high-temperature resistance, with a long-term operating temperature of 130-140°C;
High mechanical strength and UL94 V-0 flame retardancy;
Stable dielectric properties, chemical resistance, and excellent dimensional accuracy.
Typical Applications: PCB substrates, insulation support components for electrical equipment, transformer separators, etc.
Advantages: Balanced overall performance and outstanding cost-effectiveness.
Limitations: The material is brittle and burrs are easily generated during drilling.
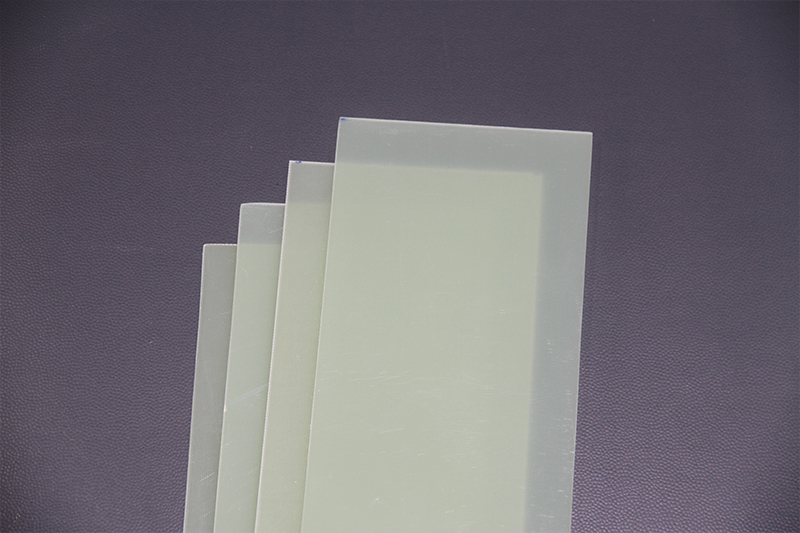

Composition: Epoxy resin + alkali-free glass cloth(it is more uniform than FR4)
Key Features:
Heat resistance reaches Class B (155°C), mechanical strength is superior to FR4, and excellent bending resistance;
Low dielectric constant, excellent arc resistance.
Typical Applications: Insulation components for high-voltage electrical appliances, motor slot wedges, precision switch insulation components, etc.
Advantages: Stable performance in high-temperature environments, suitable for precision component manufacturing.
Limitations: High production cost, processing requires specialized equipment.
Composition: Made by laminating phenolic resin with cotton fiber paper or wood pulp.
Key Features:
Low cost, easy to process (can be sawed and drilled), and has a certain degree of arc resistance;
Relatively low temperature resistance (long-term use must be kept below 105°C), high water absorption, and prone to deformation in humid environments.
Typical Applications: Low-voltage electrical enclosures, switch panels, instrument insulation gaskets, etc.
Advantages: Affordable, suitable for high-volume production of non-precision components.
Limitations: Poor environmental performance (contains formaldehyde release) and prone to carbonization in high-temperature environments.

Composition: Polyimide film or laminate as the primary material.
Core Characteristics:
Extremely high-temperature resistance, with long-term operating temperatures exceeding 260°C, radiation resistance, and chemical inertness.
Available in flexible or rigid forms, with extremely low dielectric loss.
Typical Applications: Aerospace cable insulation, FPC flexible circuit boards, and high-temperature motor insulation components.
Advantages: Optimal performance in extreme environments.
Limitations: Expensive (approximately 5-10 times that of FR4) and difficult to process.
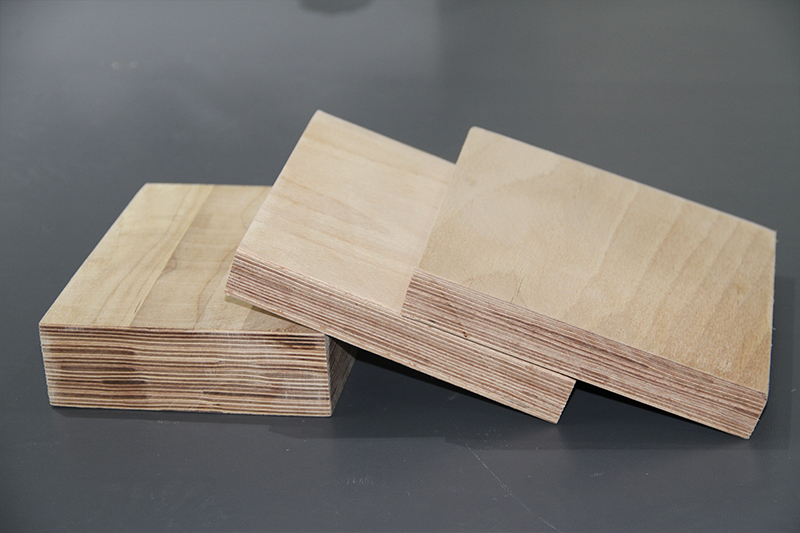
Composition: Birch+phenolic/epoxy resin
Core Characteristics:
Mechanical strength approaching that of metal, capable of precision machining such as turning, and excellent oil resistance.
Heat resistance approximately 120°C, prone to delamination in humid environments.
Typical applications: Transformer insulation stays, distribution box rails, and insulation components for mining electrical appliances.
Advantages: Lightweight and easy to process.
Limitations: Poor flame retardancy (requires additional flame retardant addition) and susceptible to moisture and mildew.

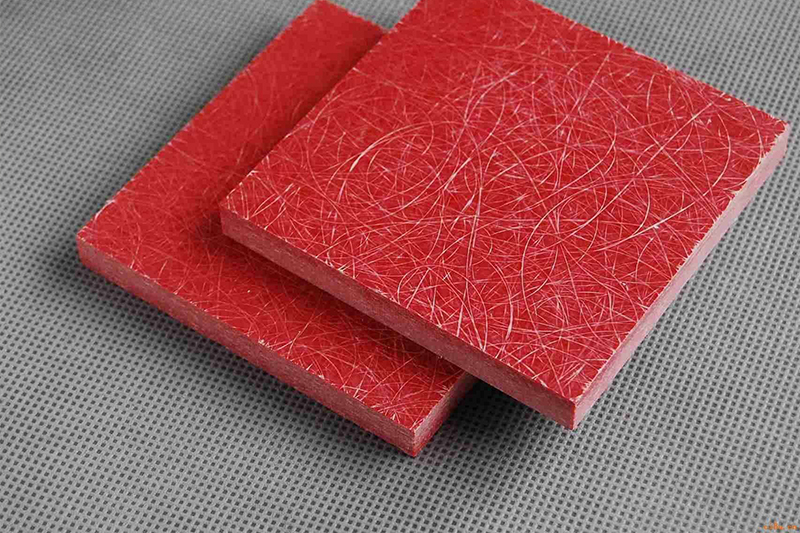
Ingredients: Unsaturated polyester resin+glass fiber mat.
Key Features:
Excellent flame retardancy (reaching UL94 V-0 rating) and outstanding arc resistance (up to 180 seconds);
Heat resistance of approximately 155°C, and stronger impact resistance than FR4.
Typical Applications: High-voltage switchgear partitions, arc shields, and rail transit insulation components.
Advantages: High fire safety, particularly suitable for high-risk arcing scenarios.
Limitations: Low material toughness and prone to degradation due to long-term UV exposure.

The above six types of insulation boards, with their unique performance advantages, play an irreplaceable role in numerous fields such as electrical, electronics. When selecting an insulation board, consider factors such as the operating temperature, voltage level, mechanical strength requirements, and cost budget to select the most suitable insulation material to ensure safe and stable equipment operation.
If you need our products please write down any questions, we will reply as soon as possible.
There are three ISO certificates for quality certification. The certificates will be shown later. ISO
After receiving the advance payment, the production cycle is 15-25 days. And the transportation cycle should be calcul……
We supply with installation guide and user manual for each transformer. If you do not understand them. We will offer v……