In electrical equipment manufacturing, the transformer industry, and motor insulation systems, both electrical pressboard and phenolic paperboard are commonly used insulating materials. Although their names are similar, their material structures, core properties, applicable scenarios, and temperature resistance ratings differ significantly. This article breaks down the differences between the two from a professional perspective, providing selection guidance for engineering technicians and purchasing personnel.
Electrical pressboard is made from high-purity insulating wood pulp through multi-layer lamination and hot-pressing curing processes. It belongs to rigid fiber insulating materials, and common types include:
Transformer Pressboard
Crepe Pressboard
High-Density Electrical Pressboard
♦ Pure cellulose structure, high electrical strength.
♦ Oil absorption meets the requirements for oil-immersed transformers.
♦ Heat resistance rating is Class A (105℃).
♦ Dimensional stability meets processing requirements, and it can be made into corner rings, pads, and various insulating structural components.
Oil-immersed transformers
Reactors
Capacitors
High-voltage insulation components
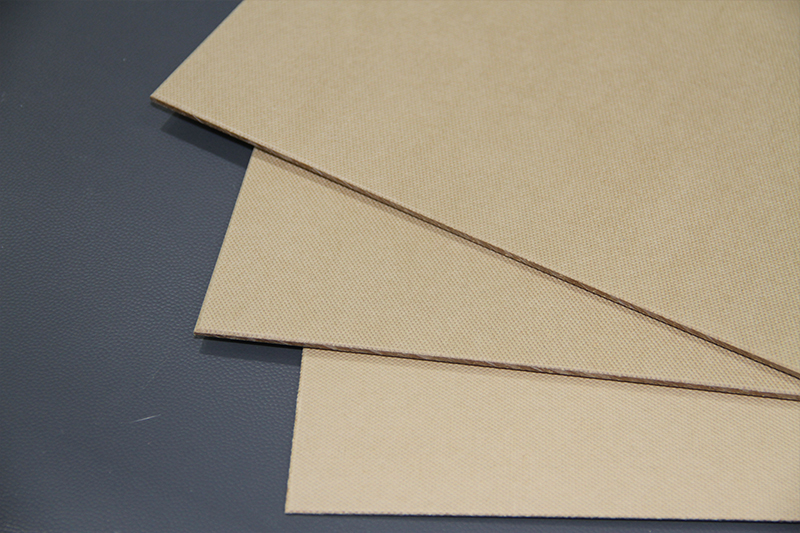

Phenolic paperboard is made by impregnating insulating paper with phenolic resin and then curing it through hot pressing. It belongs to the paper-based laminate category, and internationally common models include PFCP, XXXPC, XPC, etc.
♦ Rigidity and mechanical strength meet structural support requirements.
♦ Heat resistance reaches Class E (120℃) and above.
♦ Arc resistance and abrasion resistance are superior to ordinary paperboard.
♦ It can be cut, punched, drilled, and processed.
High and low voltage switchgear insulation components
Motor insulation gaskets
Control cabinet terminal blocks tooling fixtures and jigs
Household appliance insulation accessories
Electrical paperboard is composed of pure cellulose and molecules are linked by hydrogen bonds. It contains no synthetic resin.
Phenolic paperboard is a composite material. Cellulose fibers are coated with phenolic resin, forming a dense laminated structure.
Electrical paperboard has good toughness and plasticity, making it suitable for bending and forming processes.
Phenolic paperboard has higher hardness and impact resistance, making it suitable for structural support components.
Electrical paperboard has higher dielectric strength than phenolic paperboard. It is suitable for use in dry environments.
Phenolic paperboard has superior moisture resistance and stable electrical properties. It is suitable for use in humid environments.
Phenolic paperboard has a heat resistance temperature 30-50℃ higher than electrical paperboard, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Electrical paperboard can be processed using traditional paper processing techniques. Phenolic paperboard requires molding or machining to produce.
♦ Projects with high cost control requirements for insulation materials, such as low-voltage transformers.
♦ Dry working environment, free from high temperatures and chemical corrosion.
♦ Insulating components require manual processing or folding.
♦ Application environments with high temperatures, humidity, or chemical media, such as automotive motors and chemical equipment.
♦ Components need to simultaneously provide structural support and insulation, such as relay bases.
♦ Specific requirements for the mechanical durability of materials.
Q1: Can electrical paperboard and phenolic paperboard be used interchangeably?
A1: They can be used interchangeably in low-pressure, dry environments, but are strictly prohibited from being mixed in high-temperature and high-humidity environments.
Q2: What are the differences in the environmental performance of the two materials?
A2: Electrical paperboard is biodegradable. Phenolic paperboard, due to its resin content, is more difficult to recycle.
Q3: How to distinguish between electrical paperboard and phenolic paperboard?
A3: Phenolic paperboard has a laminated glossy surface and a resinous odor. Electrical paperboard has a texture similar to rigid paper.
Electrical paperboard is suitable for oil-immersion applications, scenarios requiring oil absorption, and structural insulation of transformers of 110kV and below.
Phenolic paperboard is suitable for insulation requirements of high mechanical strength, dry-type electrical equipment, and high-temperature environments.
When selecting transformers for a project, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the dielectric conditions, operating temperature, electrical performance indicators, and mechanical strength requirements to ensure the safe operation and service life of the equipment.
If you need our products please write down any questions, we will reply as soon as possible.
There are three ISO certificates for quality certification. The certificates will be shown later. ISO
After receiving the advance payment, the production cycle is 15-25 days. And the transportation cycle should be calcul……
We supply with installation guide and user manual for each transformer. If you do not understand them. We will offer v……