In power equipment, transformers, switchgear, new energy, and industrial electrical systems, insulating tube is a key component providing insulation protection and structural support. Its quality directly affects the safety, reliability, and service life of the equipment. In practical engineering, common problems such as insulation breakdown, tubing cracking, and accelerated aging are mostly related to quality defects in the insulating tubing.
So, what factors affect the quality of insulating tubing? This article analyzes the factors from the perspectives of raw materials, production processes, structural design, quality inspection, and the usage environment, providing selection references for purchasing and technical personnel.
Commonly used materials for insulating tubing include epoxy resin, phenolic resin, polyester resin, and glass fiber. If these materials themselves are of poor quality, such as impure resin, insufficient heat resistance, or easy aging, it will directly lead to low voltage withstand capability, brittleness, and cracking of the product.
If the glass fiber cloth, paper, or other materials used have problems, such as uneven glue content or inconsistent weaving density, it will seriously affect the final performance of the tubing.
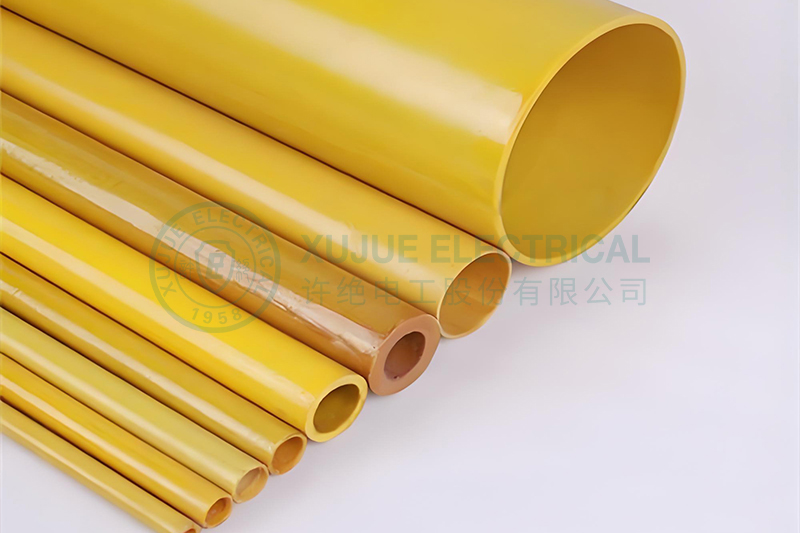

If the resin is not thoroughly impregnated or air bubbles are not completely removed during pultrusion, winding, or molding, it will lead to:
Internal voids or delamination
Easily causing partial discharge
Deteriorated mechanical strength
Inaccurate control of temperature and time during curing will lead to:
Incomplete resin curing
Excessive internal stress
Easily causing changes in pipe dimensions
Different voltages and applications require different tube wall thicknesses. Incorrect selection can lead to:
Insufficient insulation thickness and inadequate safety margins
More susceptible to voltage breakdown
When used in transformers and switches, tubes not only withstand voltage but also pressure and vibration. If these forces are not properly calculated during design, they are prone to deformation and breakage after long-term operation.
Qualified tubes must undergo the following tests before leaving the factory:
Voltage withstand test
Partial discharge test
Bending, compressive, and tensile strength tests
If these tests are not performed or are not performed correctly, substandard products may be produced.
If the raw materials used in production are of poor quality, the process is unstable, and there is no strict batch management, the performance of each batch of products will vary, thus affecting the reliability of the entire project.
When insulation pipes are stored or used for long periods in high-temperature, humid, or environments with large temperature fluctuations, they tend to absorb moisture more easily. This accelerates aging and leads to a decline in insulation performance.
In chemical plants, power plants, and similar facilities, insulation tubes may come into contact with oils, acids, alkalis, or corrosive gases. If the material lacks sufficient chemical resistance, its service life will be significantly reduced.
During handling, storage, or installation, insulation pipes may encounter the following issues:
Impact damage or compression
Long-term storage in damp or humid environments
Irregular cutting or drilling during installation
These factors can also cause permanent damage to the pipes and negatively affect their performance and service life.
To ensure long-term, stable performance of insulation pipes in engineering applications, the following measures are recommended:
♦ Select reliable raw materials and proven material formulations
♦ Adopt stable and well-controlled forming and curing processes
♦ Choose appropriate pipe types based on equipment voltage ratings and application scenarios
♦ Establish full-process inspection and quality traceability systems
♦ Implement customized design and protective measures according to specific operating environments
Visual inspection: The surface should be smooth and even, with uniform color and no bubbles or cracks.
Dimensional measurement: Use calipers to check the wall thickness; deviations should be within allowable tolerances.
Performance testing: Verify mechanical strength through bending, compression, and similar tests.
Certification review: Check product certifications and third-party test reports.
The quality of insulation pipes is influenced by raw materials, manufacturing processes, structural design, testing, and the operating environment. Only through systematic control of the entire process—from production to actual use—can the safe, stable, and efficient operation of power equipment and industrial systems be ensured.
For the selection of insulation pipes in transformers, switchgear, and high-voltage electrical projects, understanding the above quality-related factors helps reduce operational risks and improve overall project quality.
If you need our products please write down any questions, we will reply as soon as possible.
There are three ISO certificates for quality certification. The certificates will be shown later. ISO
After receiving the advance payment, the production cycle is 15-25 days. And the transportation cycle should be calcul……
We supply with installation guide and user manual for each transformer. If you do not understand them. We will offer v……