EPGC203, G10, and FR4 are all made from alkali-free glass fiber cloth (E-glass) as the reinforcing substrate and epoxy resin as the binder. They are manufactured through a high-temperature and high-pressure lamination process. All three belong to thermosetting composite materials, featuring high mechanical strength, excellent electrical insulation, and outstanding chemical resistance, making them widely used functional materials in industrial applications.
Standard supply range: 0.5 mm – 50 mm.
Custom thicker sheets can be produced to meet structural support and insulation requirements in different scenarios.
Main sheet sizes include 1020 mm × 1220 mm (4 ft × 4 ft), 1220 mm × 2800 mm, etc.
Sheets can also be cut according to processing needs, ensuring compatibility with various equipment and components.
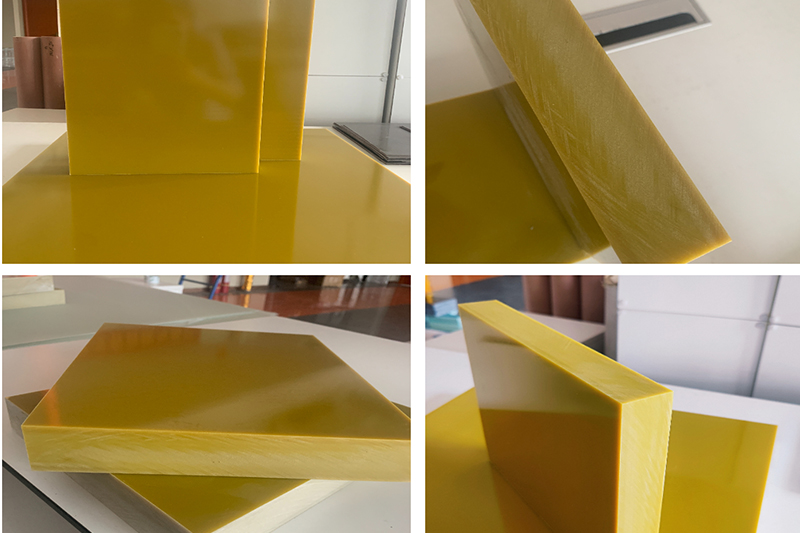
Natural: Translucent light yellow or amber, the original color of the material without added pigments.
Customized: Colors such as green, blue, red, and black can be produced with special dyes.
(Note: The common green color of PCB boards does not come from the base material itself, but from the solder mask ink applied on the surface.)
When used as a base material for printed circuit boards (PCB), sheets are typically laminated with copper foil on one or both sides.
Common copper foil thicknesses are 1 oz and 0.5 oz , meeting different current-carrying capacities and signal transmission requirements.
The key distinction among the three materials lies in the standard systems they follow, which directly determine their application focus:
EPGC203: Complies with the Chinese national standard (GB/T 1303.1-2017), mainly targeting the domestic electrical insulation and mechanical structure market.
G10: Meets the U.S. NEMA standard (LI-1-1998), recognized as a globally used high-performance epoxy glass fiber laminate, widely applied in electronics and mechanical industries.
FR4: An improved version of G10 with added flame-retardant properties, conforming to the U.S. UL standard (UL94 V-0). It is the mainstream substrate material in the PCB (Printed Circuit Board) industry.
These three materials, with their combined multi-performance advantages, have become the preferred choices in industrial applications. Their core properties include:
Reinforced with multilayer glass fiber fabric, they exhibit outstanding resistance to impact, bending, tensile, and tearing forces. The structure is strong and durable, capable of withstanding long-term mechanical stress without damage.
Even under harsh conditions such as high temperature and high humidity, they maintain excellent insulation performance, effectively preventing current leakage, making them a core choice for insulating components in electrical equipment.
With very low water absorption rates, they resist moisture penetration in humid environments, preventing significant deterioration of electrical and mechanical properties. This makes them suitable for scenarios with fluctuating humidity.
With a glass transition temperature (Tg) typically ranging from 130°C to 180°C, they can withstand high temperatures during electronic manufacturing processes such as wave soldering and reflow soldering, without deformation or failure caused by rapid temperature rise.
In environments with temperature and humidity fluctuations, FR4 shows almost no deviation in shape or size. This property is crucial for components such as PCBs that demand high precision, ensuring stable assembly and reliable operation of equipment.
FR4 resists most solvents, acids, and alkalis, preventing damage from chemical corrosion. This extends its service life in complex environments such as chemical plants and electronics manufacturing.
Despite its hardness, FR4 can be precisely shaped through CNC machining, drilling, milling, stamping, and cutting, making it adaptable to parts with different structural requirements.
One of FR4’s core advantages is its flame-retardant property, compliant with UL94 V-0 standards. It can self-extinguish within seconds after leaving an open flame, effectively preventing fire spread and meeting the strict safety requirements of electronic devices.

This is the most fundamental application of FR4. Nearly all consumer electronics (such as smartphones and computers), communication equipment, and industrial control devices use FR4 as the insulating substrate in double-sided and multilayer PCBs, providing both electrical insulation and structural support.
Transformer insulation boards, motor slot wedges, and insulating gaskets.
Partition boards and brackets in switchgear.
Electrical testing fixtures and jigs.
Support plates, layers, and baffles in equipment.
Wear-resistant insulating parts in robots and automation systems.
EPGC203, G10, and FR4 epoxy glass fiber laminates are high-performance composite materials with balanced mechanical strength, electrical insulation, heat resistance, and machinability, making them multifunctional materials widely used in industrial applications.
These laminates offer a comprehensive performance profile and broad applicability. They perfectly balance mechanical strength, electrical insulation, thermal resistance, and ease of processing:
G10 is ideal when extremely high mechanical strength and electrical insulation are required, but flame retardancy is not critical.
FR4 is the standard choice for electrical and electronic applications where flame-retardant safety is essential. It serves as a foundational material indispensable to the modern electronics industry.
If you need our products please write down any questions, we will reply as soon as possible.
There are three ISO certificates for quality certification. The certificates will be shown later. ISO
After receiving the advance payment, the production cycle is 15-25 days. And the transportation cycle should be calcul……
We supply with installation guide and user manual for each transformer. If you do not understand them. We will offer v……